

Population Momentum
Tasks
Population Change
Tasks
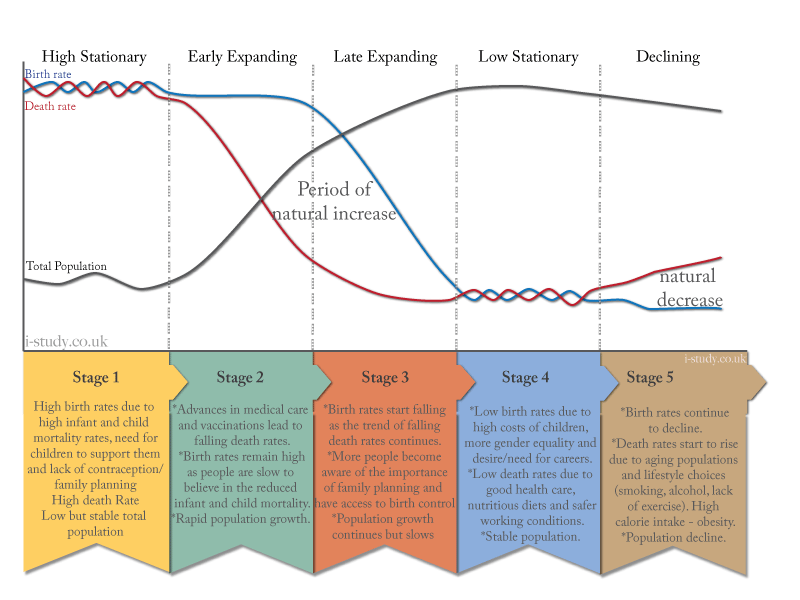
What?
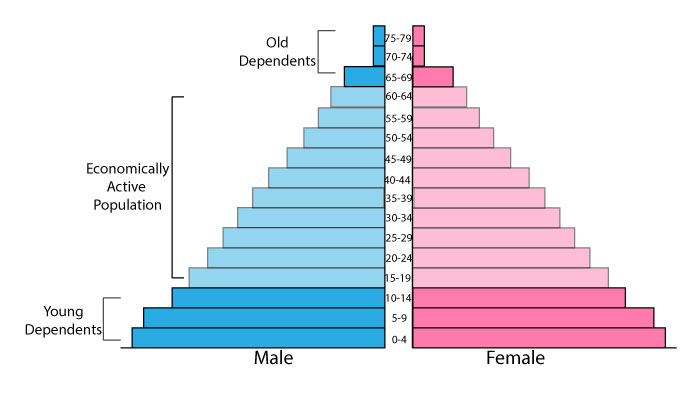
Population Pyramids are a way of displaying the demographic make up of a country in a simple graph. They show the number of males and females in each age group.
Importance
Population pyramids are important because they allow governments to predict future population patterns and plan for the changes. They also give a good indication of the level of development in a country.
Tasks
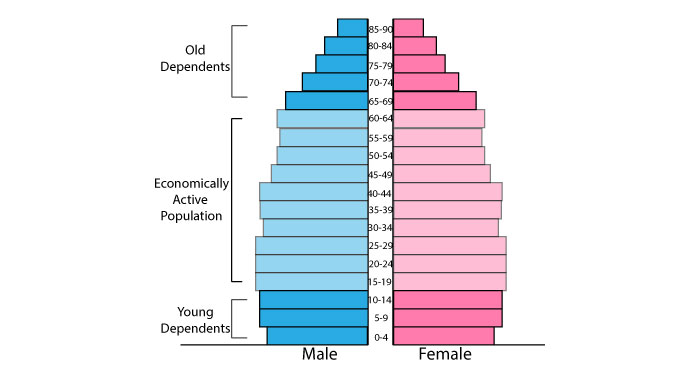
Ageing populations
Ageing populations occur when there are an increasing proportion of elderly people in a country, due to longer life expectancy and falling birth rates. It is a demographic issue that is facing most of the worlds developed countries
Ageing populations bring some significant challanges for economies, but they also bring benefits.
Tasks
Antinatalist; China
Tasks
Antinatalist; Thailand
Tasks
Pronatalist; Japan
Tasks
International Migration Flows
Tasks
For each of the following continents, describe the main migration patterns both internally and externally.
Describe and explain the flow of remittances.
International Migration Case Study
Objective: Be able to describe a recent flow of international migration and explain the causes and consequences at source and destination.
Task
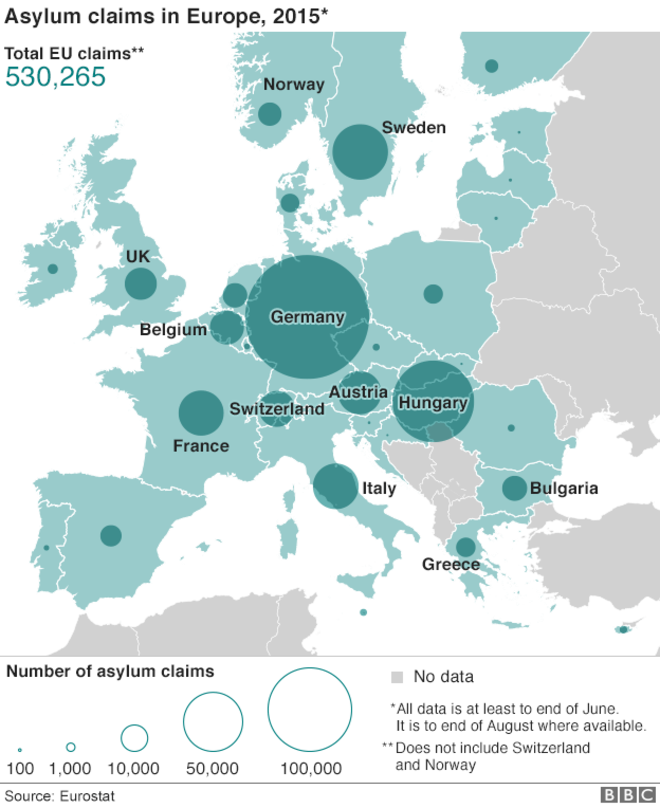
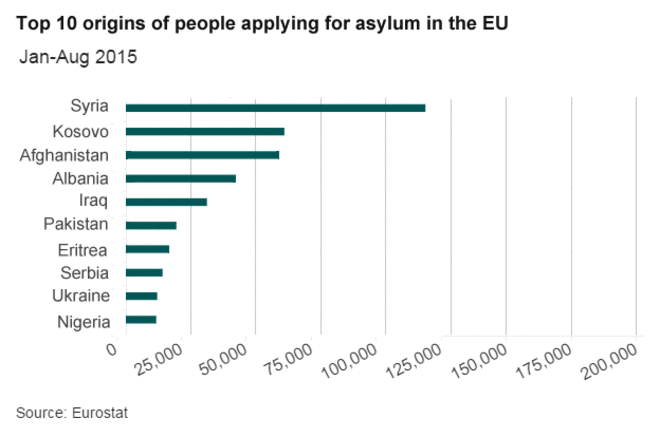
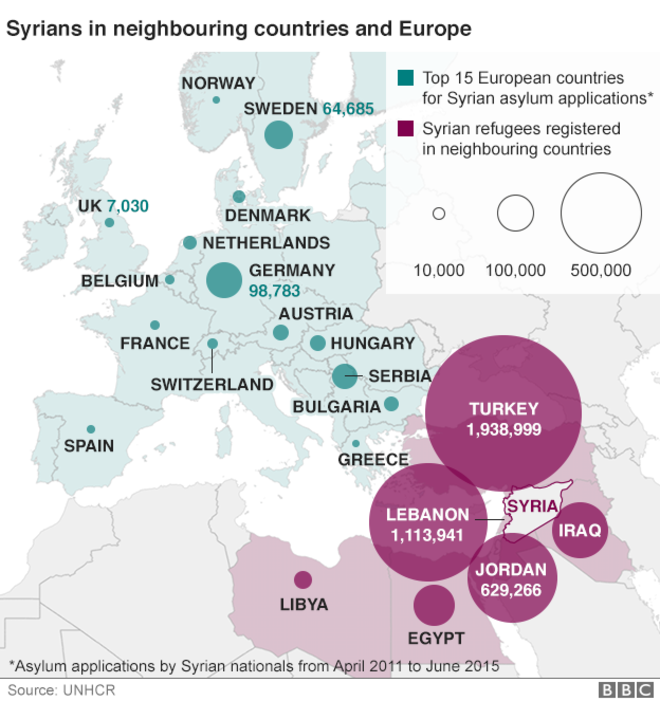
Produce a case study about the recent/current large migration into Europe. You should break your case study into the the following sections:
BBC: Migration crisis explained in graphics
BBC: Difficulty of a European solution to refugees
Guardian: Europes walls are going back up
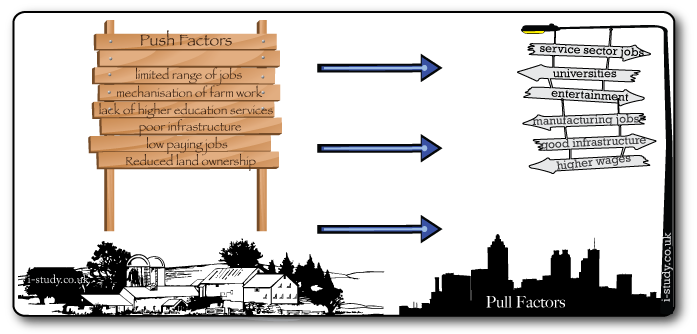
Rural to Urban Migration
The movement of people from the countryside into urban areas.
This process is happening most rapidly in developing countries as people seek employment in towns and cities. The worlds fastest growing cities are in developing countries and the majority of the the worlds megacities are also located there.
You should be able to explain the trend by referring to push and pull factors.
Case Study: China Internal Migration
Tasks
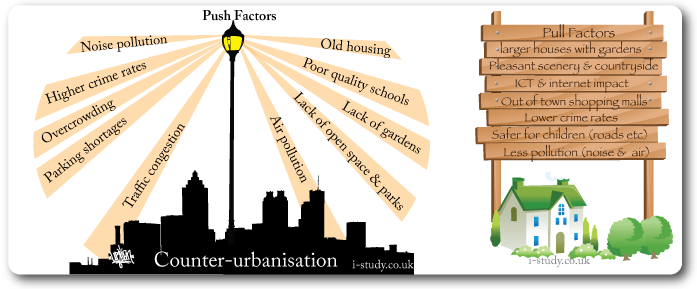
Counter-Urbanisation
This is the movement of people out of towns and cities to live in the surrounding rural areas.
This process is occurring mainly in developed countries as people commute into work from rural villages. The development of the internet has allowed increased remote working.
Decentralisation of many retail and office jobs has also led to people moving out of towns.
Gender Inequality
Tasks
2014 Global Gender Gap Index country Rankings